| Sustainable Development Goals |
Risk and Crisis Management
Enterprise Risk Management
PTT recognizes the critical importance of effective risk management in navigating the changes brought about by both internal and external factors that may impact its business. To address this, PTT adopts the internationally recognized framework set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO-ERM 2017) for ongoing risk management. This approach is embedded as a fundamental component of all business processes at PTT, ensuring seamless integration across all levels. As a result, PTT effectively integrates systems of corporate governance, risk management, and compliance with laws and regulations (Governance, Risk, and Compliance: GRC). This integration enables the Company to support executive decision-making, mitigate risks, and create added value for the organization in a systematic and efficient manner.
Enterprise Risk Management Policy
PTT has established a comprehensive Enterprise Risk Management Policy and a corresponding Risk Appetite Statement (RAS) to guide its risk management practices. These documents are regularly reviewed and updated to ensure alignment with evolving factors, including global standards, best practices, as well as the Company’s vision, mission, and strategic goals. Once endorsed and signed by the Chairperson of the Enterprise Risk Management Committee, the policy and RAS are formally communicated across the organization to ensure adherence by all PTT employees.
Governance
The PTT Board of Directors places significant emphasis on ensuring that PTT operates as an efficient and high-performing organization. The Board actively supports the integration and systematic management of risks through a robust governance framework, which encompasses Governance Risk and Compliance (GRC). To facilitate this, the Board has delegated responsibility to various committees, including the Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee (CGSC) at the board level and the Governance Risk Compliance and Sustainability Management Committee (GRCMC) at the management level. These committees are tasked with overseeing the implementation of governance principles, operational risk management, internal controls, legal and regulatory compliance, and sustainability efforts. They also focus on efforts in social responsibility, community engagement, and environmental stewardship, as well as promoting ethical conduct and preventing corruption and misconduct in PTT's operations. Furthermore, PTT has established the Enterprise Risk Management Committee (ERMC) at the board level and the Corporate Plan and Risk Management Committee (CPRC) at the management level. These committees oversee the organization’s enterprise-wide risk management strategy. They regularly report on the progress of governance, risk management, internal controls, and legal compliance to the relevant committees for review, ensuring continuous improvement in effectiveness and efficiency within the set timelines.
The PTT Board of Directors approved the establishment of the Enterprise Risk Management Committee (ERMC) on November 5, 2024. As of December 31, 2024, the ERMC comprises three independent directors from the PTT Board. The Senior Executive Vice President, Corporate Strategy has been appointed as both the Chief Risk Officer (CRO) and Chief Stakeholder Officer (CSO), and serves as the Committee's secretary.
The Senior Executive Vice President, Corporate Strategy (SEVP), who also chairs the Corporate Plan and Risk Management Committee (CPRC), is responsible for implementing the policies, feedback, and recommendations provided by the ERMC. This includes overseeing the Comprehensive risk management strategy and ensuring the alignment and effective execution of risk management and stakeholder engagement practices across the organization. The ERMC’s performance is reported to the Board of Directors on a quarterly basis.
The Executive Vice President of the Internal Audit Department is responsible for evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of corporate governance, risk management, and internal control processes, providing regular reports to the Board of Directors at least on a quarterly basis.
To enhance the effectiveness of Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance with Laws, Regulations, and Organization Rules Policy (GRC), PTT has implemented a governance framework based on the "Three Lines Model." This approach emphasizes the importance of ensuring that all individuals understand and rigorously follow the rules and their specific responsibilities. It focuses on proactively preventing and addressing issues faced by employees through a well-structured, systematic process. Additionally, the model ensures a clear segregation of duties, including approvals, reviews, audits, and asset management responsibilities, to avoid conflicts of interest and ensure proper checks and balances within the organization. The detailed roles and responsibilities are outlined as follows:
First Line – Process Owners: Employees responsible for executing their own tasks and overseeing the work of their subordinates to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, organizational objectives, and effective risk management.
Second Line – Policy Makers: Departments or committees responsible for governance, tasked with setting organizational standards, policies, regulations, and practices. They provide guidance, communicate effectively, support operational implementation, and manage risk across the organization.
Third Line – Operational Auditors: Internal auditors, functioning as an independent unit, report directly to the Audit Committee and indirectly to the CEO and the Executive Vice President. Their role is to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of internal controls, corporate governance, risk management, and operations across the First and Second Lines by adopting a risk-based audit approach.
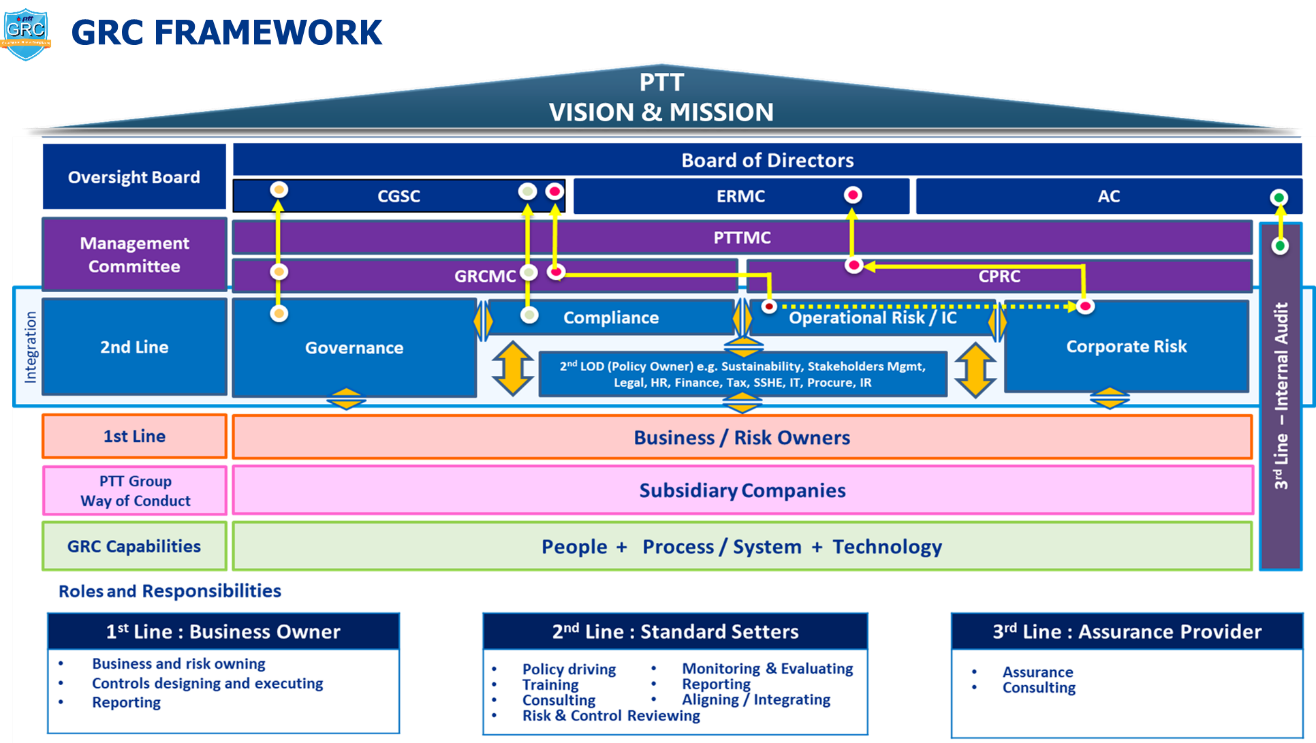 PTT GRC Framework |
The Performance, Risk, and Investment Evaluation Department operates under The Senior Executive Vice President, Corporate Strategy, with a structure independent from business units to ensure impartiality. Its key responsibilities are as follows:
- Implement the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework and policies to ensure alignment with PTT's strategic goals and business objectives.
- Analyze and assess risks to identify material risks, and present them to the CPRC, ERMC, and the PTT Board of Directors, respectively.
- Oversee the effectiveness and consistency of risk management processes throughout PTT.
- Monitor, track, and report on risk incidents and the effectiveness of risk management efforts to the CPRC and ERMC.
Fostering an Organizational Risk Culture
PTT has developed a comprehensive strategy to promote a strong and effective risk culture across the organization, embedded within its GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) framework. This strategy integrates principles of good corporate governance, ethical standards, and business conduct with robust risk management, internal controls, and regulatory compliance. By communicating these principles through various channels, PTT aims to enhance employees' understanding of GRC, instilling a deep sense of awareness and fostering a culture of risk management throughout the Company. Key to this approach is the optimal allocation of resources to continuously improve enterprise risk management practices. PTT supports this goal by offering a range of GRC-related training programs and organizing activities that reinforce the culture, such as GRC Talks at monthly PTT Management Committee (PTTMC) meetings. These discussions are also incorporated as a standing agenda item in department meetings. In addition, PTT hosts GRC Forums, where executives and external experts share insights and experiences, helping to further cultivate the GRC culture across the workforce. The Company also promotes RM&IC (Risk Management and Internal Control) Knowledge Awareness through various initiatives, including the widespread dissemination of GRC policies and educational content. Key documents, such as the Enterprise Risk Management Handbook, along with other communication materials, are shared via the Risk Management Dashboard (RMD). PTT actively engages directors, executives, and employees by providing platforms for submitting feedback on risk management practices, which are then analyzed to address potential future risks. Furthermore, PTT conducts annual surveys to gauge the level of understanding and awareness of risk management across the organization.
PTT has established multiple communication and reporting mechanisms to enable employees to proactively identify and report potential risks, as well as to contribute suggestions. These channels include:
- Whistleblowing: Website: https://whistleblowing.pttplc.com/, Email: corporate@pttplc.com, and mail.
- Agenda-Based Meetings: Risk management and related topics, such as GRC Talks, are regularly reported alongside performance results.
- Suggestion System: Employees are encouraged to submit suggestions for enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of work processes.
- Sub-Standard/Near-Miss Reporting System: Employees are empowered to report activities that could potentially lead to asset loss or injury.
PTT ensures that all independent directors undergo regular risk management training. All independent and external directors (100%) have completed either the Director Certification Program (DCP) or the Director Accreditation Program (DAP) offered by the Thai Institute of Directors (IOD). These programs cover essential topics such as risk management and good corporate governance (GRC). Additionally, PTT provides an orientation program for new directors, helping them gain a comprehensive understanding of PTT’s business operations, as well as relevant laws and regulations.
As of December 31, 2024, PTT's Board of Directors comprises 15 members, each possessing expertise and experience in business management and corporate governance.
- Independent Directors: 80%
- Executive Directors: 7%
- Non-Executive Directors: 13%
All 15 directors bring specialized knowledge in political science and risk management.
Directors appointed to the Enterprise Risk Management Committee (ERMC) are provided with comprehensive internal orientation programs to support their roles in risk management and stakeholder engagement. These orientations cover risk management standards, policies, frameworks, organizational structures, and PTT’s strategies for risk identification and mitigation, ensuring that the ERMC is fully equipped to effectively oversee and evaluate risk management processes.
PTT has established the PTT Group Leadership and Learning Institute (PLLI) with the goal of developing employee capabilities, fostering a culture of continuous learning, and spreading knowledge about risk management throughout the organization. This is achieved through targeted training programs and the distribution of key risk management resources, such as the Risk Management Handbook and the Knowledge Management Portal.
Furthermore, PTT has integrated financial incentives with risk management performance indicators, as outlined in its core values: SPIRIT. These values are pivotal in shaping the behaviors and collaborative work practices of both executives and employees. The inclusion of risk management in the SPIRIT values serves to promote awareness and knowledge of risk management across the organization, helping employees recognize and manage risks in the workplace. The key components of the SPIRIT values are as follows:
I – Integrity & Ethics: Fostering a culture of integrity by encouraging employees to act with honesty, transparency, and ethical conduct. Employees are expected to perform their duties in accordance with high moral standards and to be mindful of the risks that exist in the workplace.
P – Performance Excellence: Striving for excellence by encouraging employees to embrace change, adapt quickly, and consistently exceed expectations to deliver exceptional value to stakeholders.
The organization’s values are also used as a basis for performance evaluation. Employees are expected to demonstrate success that aligns with PTT's SPIRIT values, which influences decisions related to promotions, salary adjustments, and both fixed and variable bonuses.
PTT employs Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) as a vital tool for managing organizational performance, ensuring alignment between the goals of both leadership and employees. This approach encourages employee engagement in risk management. Examples of KPIs related to risk management include organizational risk management effectiveness and the success of price risk mitigation efforts, among others.
Risk Management Process
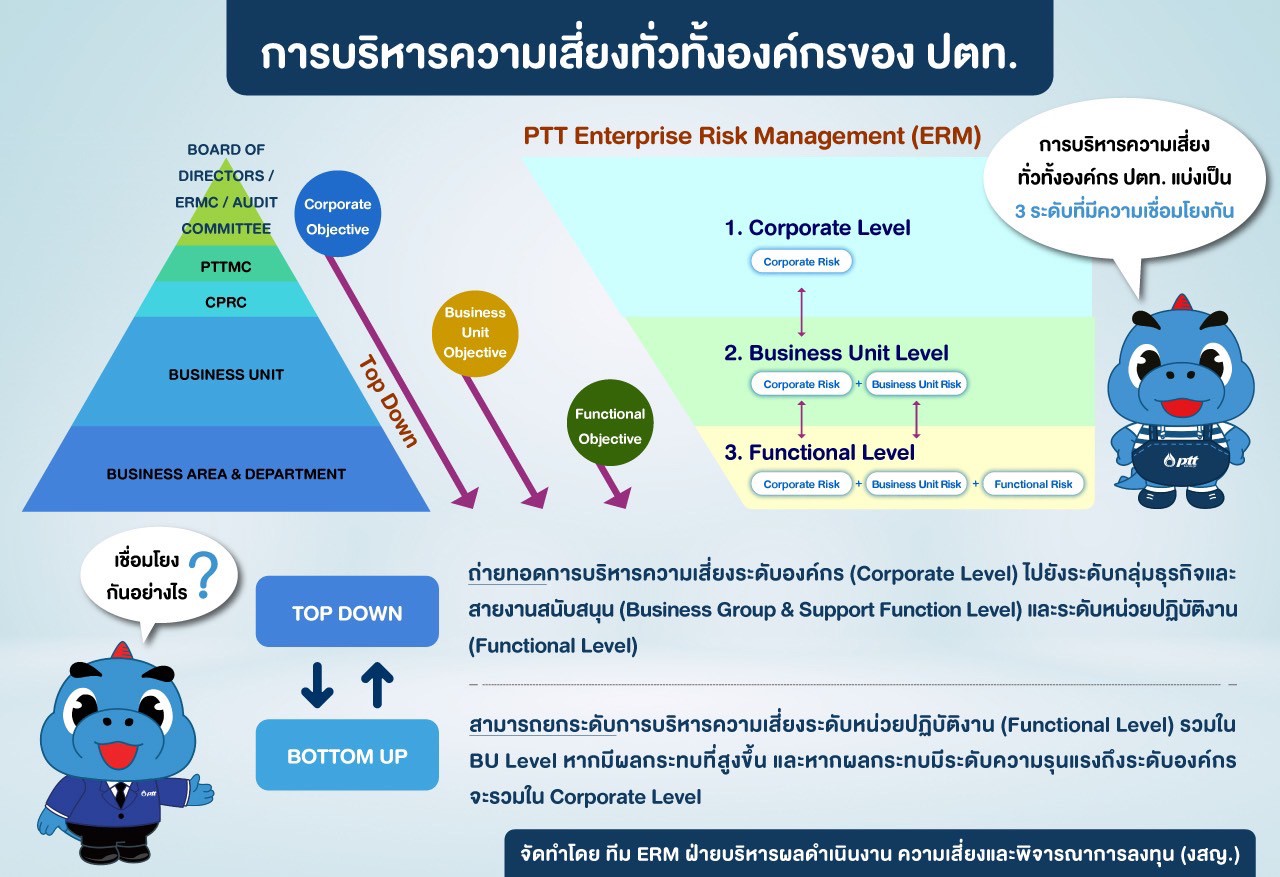
PTT adopts a systematic approach to risk management, overseen by various management committees, and integrates risk management into the enterprise planning process. This ensures that the risk management plan is not only effective but also aligned with the organization’s goals and strategies. PTT’s risk management framework operates seamlessly across three levels: the corporate level, business group level, and operational level. At the operational level, risk management is considered the responsibility of every department, with oversight from senior management to ensure that risks are controlled within acceptable limits. This responsibility is clearly defined in the job descriptions for each unit. Furthermore, PTT has established a comprehensive risk management process through the "PTT Enterprise Risk Management Manual (ERM)." This written manual serves as the organization-wide standard for risk management practices. It includes an integrated approach to enterprise-wide risk management, definitions and terminology, and PTT’s risk management framework, and detailed procedures for managing risks across the organization.
 |
PTT’s risk management process is routinely evaluated by its internal departments, including the Corporate Management Systems Division and the Internal Audit Division. Furthermore, it undergoes an annual review by PTT's Audit Committee and external audit by the State Enterprise Policy Office (SEPO) to ensure compliance and effectiveness.
In 2024, PTT implemented its enterprise risk management process in line with the criteria and performance evaluation system for state-owned enterprises. Furthermore, the process was enhanced following a review by the Enterprise Risk Management Committee, as outlined below:
- Reviewed and updated the "Risk Management Policy" and the "Risk Appetite Statement" to ensure alignment with changing circumstances.
- Assessed the impact of the business plan on stakeholders, leading to the development of action plans to mitigate any negative impacts through appropriate management strategies.
- Supervised the management of corporate innovation to ensure comprehensive implementation, aiming to increase innovation effectiveness that aligns with PTT’s strategic objectives and key goals.
- Provided input on major investment projects and long-term contracts that involve complex business risks and could significantly impact PTT, before presenting them to the PTT Board for approval.
- Reviewed the annual corporate risk register before submitting it to the PTT Board for approval, alongside the annual business plan, ensuring that the risk management plan is integrated with the business plan for better clarity and alignment with business direction, goals, and strategies, while ensuring its execution throughout the organization.
- Closely monitored risk management on a quarterly basis by setting risk indicators to detect early warnings, as well as measuring the effectiveness of risk management. Feedback was provided to management to review the risk management plan in response to evolving strategies and business conditions, with results reported to the PTT Board.
- Evaluated risk assessment outcomes, the severity of impacts, and developed mitigation measures for significant events that could affect the operations of the PTT Group (Risk Events). Feedback or policies were provided to further strengthen risk management planning.
- Enhanced the risk management strategy for price risks by utilizing derivative instruments within the PTT Group companies.
Risk Management Tools
PTT researches and applies a variety of risk management tools, including:
- Establishing the Organization’s Risk Appetite (PTT Risk Appetite), which serves as a framework for the organization’s operations. The 4 key components of this framework are as follows:
1. Strategic Risk concerning energy security and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Compliance Risk related to good corporate governance, legal compliance, and adherence to relevant regulations.
3. Operation Risk focusing on the efficient conduct of business, delivering quality products and services, mitigating SSHE impacts, and maintaining cybersecurity.
4. Financial Risk related to the PTT Group's investment returns, creating value, managing financial risks appropriately to maintain financial stability, and preserving credit ratings.
For the Corporate Risk Profile, PTT develops a Risk Management Plan (Control & Mitigation Plan), along with annual Key Risk Indicators (KRI) and defined acceptable risk levels. These are communicated to relevant stakeholders to ensure alignment. Regular monitoring is conducted to ensure that the organization’s risk levels do not exceed the predefined acceptable limits.
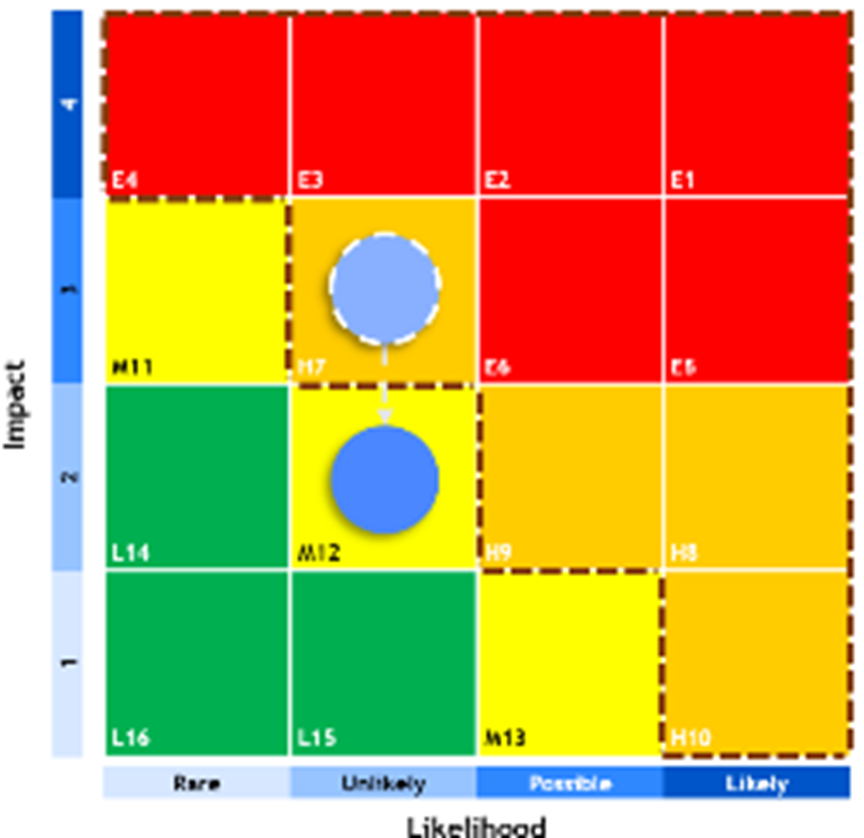
- Risk Assessment and Prioritization using a Risk Map, which identifies the severity of both the likelihood and impact of risks in relation to the organization’s defined risk boundaries (Risk Boundary). Risks are categorized into four levels: Low Risk (Green), Moderate Risk (Yellow), High Risk (Orange), and Very High Risk (Red), as shown in the diagram.
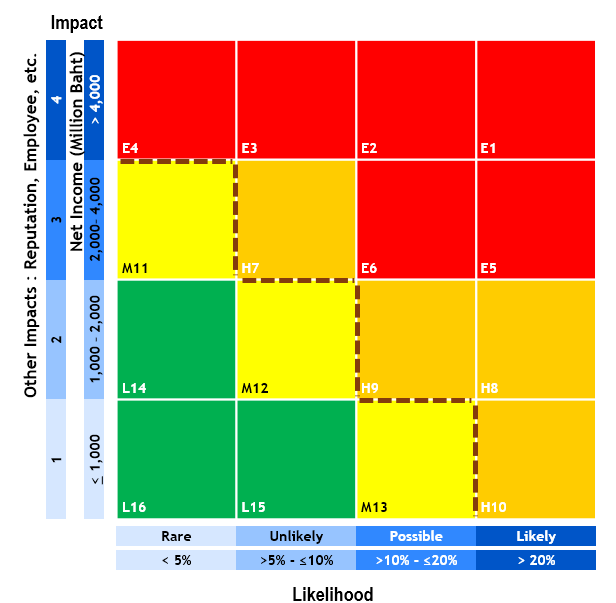
- Monte Carlo Simulation is utilized to assess the potential impact on financial performance, specifically through Value at Risk (VaR). This analysis considers key risk factors that influence PTT Group’s performance (net profit), such as the prices of petroleum and petrochemical products, refining margins, exchange rates, and production volumes. The data and assumptions used in the analysis are drawn from international industry research and economic forecasts. Additionally, a Sensitivity Impact Analysis is conducted to evaluate how changes in each key risk factor affect the organization under various scenarios. This process is carried out quarterly, enabling PTT to proactively update and refine its risk management plan to improve its overall effectiveness.
Enterprise-Level Risk Management
PTT assesses risks affecting its operations (Risk Universe), considering both internal and external factors. Internal factors include feedback from the Board of Directors, subcommittees, the executive leadership team, as well as the organization's key goals and strategies. External factors encompass the needs and expectations of stakeholders, economic, social, political, and technological trends, industry competition, and an annual evaluation of material sustainability issues (Material Assessment) based on the principle of Double Materiality. This involves examining both risks and opportunities that impact the environment, society, and governance, with a focus on human rights throughout the organization’s operations (Impact Materiality). Additionally, it considers the financial impact of external factors on the organization’s performance (Financial Materiality). Sustainability risks (ESG Risks) related to key material issues, which are prioritized at a high level, are integrated into the enterprise-level risk management process each year. These risks are managed through the established processes of the responsible departments.
The Enterprise Risk Management Plan (Control and Mitigation Plan), once approved by PTT’s Board of Directors, will be closely monitored on an ongoing basis. In the event of a Trigger Alert, the responsible unit (Risk Owner) must prepare relevant data and an updated risk mitigation plan. This plan will be presented to the Enterprise Planning and Risk Management Committee (CPRC) and the Enterprise Risk Management Committee (ERMC) for review and approval. Once approved, corrective actions will be promptly implemented to restore the risk level to an acceptable threshold.
Furthermore, PTT mandates the use of Control-Self-Assessment (CSA) across all processes to ensure that effective internal controls are consistently applied. Process owners must fully understand the risks associated with their processes or activities and assess the adequacy of the existing controls. If residual risks exceed acceptable limits, process owners are responsible for designing and implementing additional controls to reduce the impact or likelihood of those risks to an acceptable level. Management is tasked with overseeing and continuously improving the effectiveness of these controls. The outcomes of the CSA are compiled by the Internal Control and Risk Management Department for analysis of control effectiveness. These findings are reported to the relevant committees, who provide feedback, suggest improvements, and approve the CSA plan for the following year.
Examples of 2 topics for identifying risks of PTT (considering opportunities and impacts), including mitigation measure
Exposure |
Risk Management Approach |
Acceptable Risk Level After Management (Risk Movement) |
Acceptable Risk Level (Risk Appetite) |
|
| 1. Risk from Reduced Natural Gas Production and Supply Continuity: Natural gas reserves in both Thailand and Myanmar have been declining due to over 30 years of production. As these fields enter the post-plateau phase, producers are allowed to reduce their gas delivery commitments under contract, which increases the likelihood that producers may not be able to meet agreed-upon delivery volumes. Additionally, ongoing political instability in Myanmar presents a further risk of disruption to the flow of natural gas from Myanmar to Thailand. |
|
|
PTT customers receive natural gas continuously, without disruptions in the electricity system. | |
| 2. Cybersecurity Risks: The organization faces various cybersecurity threats, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, cyber extortion, and damage to its reputation and brand image. These risks can result in business interruptions. |
|
|
In the event of a cybersecurity incident. |
In addition, PTT has acknowledged and considered emerging risks, with the following details:
Emerging Risks |
The speed of AI technology adoption could outstrip the speed of AI governance development |
Geopolitical uncertainties |
|
Risk Details |
A risk exists that PTT’s AI governance may not be able to keep up with the company’s growing use of AI. With advancements in AI technology happening at an unprecedented rate, its pace of adoption has the potential to outstrip the company’s capacity to effectively manage its use due to factors such as a lack of technical expertise or employee talent gaps. As the usage of AI technology expands across various business functions and new regulations are announced to govern its’ development and implementation, it is becoming a challenge for companies to update their AI governance processes and policies in a timely manner. The importance of AI is reflected by the inclusion of the energy sector as one of the target sectors for Thailand’s National AI Strategy and Action Plan (2022-2027). This plan aims to foster the development and adoption of AI in the country by setting targets and actions plans through collaboration between the public sector, private sector, and educational institutions. This includes developing laws and regulations around AI, developing national infrastructure for sustainable AI development, increasing human capability and improving AI education, driving AI technology and innovation development, and promoting the use of AI in the public and private sector. |
Recent changes in the global political landscape have resulted in increased geopolitical uncertainties due to factors such as an increase in national security concerns, shifting global alliances, and shifts in trade flows. Examples of uncertainties include the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict, tensions in the Middle East, growing tensions between the US and China, and US trade policies under the new Trump administration. As a state-owned enterprise, it is PTT’s responsibility to manage resources to ensure energy stability within the country. |
|
Impacts |
If PTT does not have AI governance that can effectively manage the company’s use of AI, the company could potentially face multiple impacts. The number of data breaches resulting from vulnerabilities in AI models could increase as a larger variety of AI models becomes available and used. There is also the potential that through AI misuse, fake information derived from generative AI models may be used in communications with clients leading to misinformation. Increases in data breaches and misinformation resulting from the mismanagement of AI can lead to reputational damages and legal action in some cases. |
For companies in the oil and gas industry, this has the potential to lead to supply chain disruptions as political instability and conflicts affect the availability and cost of materials and machinery, volatile fluctuations in the price of oil and gas impact profitability, and changes in trade flow impact strategic planning. For example, increased costs from supply chain disruptions affect the ability to replace machinery and increase costs, the failure to hedge for significant price fluctuations for material such as crude oil and natural gas or machinery could result in reduced profits., and changes in global alliances and shifting trade flows can lead PTT reassess strategic priorities and operational footprint, leading to decisions such as changes in PTT’s key trade partners in the future. On the other hand, geopolitical tensions have exerted upward pressure on global oil prices, which could have a positive impact on certain companies within PTT Group. |
|
Mitigation Measures |
To mitigate AI governance risks, PTT adopts a selective and secure approach to AI deployment. Internal platforms such as ABDUL (AI knowledge Mining) are developed on RAG-based architecture to ensure traceability and control, while external SaaS tools like OLAF (AI Meeting Transcription) and Copilot are carefully vetted to ensure no internal data is stored or used for model training. All AI services must comply with strict data privacy and confidentiality standards. PTT also emphasizes employee readiness through targeted PR campaigns and continuous training to build AI literacy and responsible usage. In parallel, the company is finalizing a comprehensive AI Governance Framework aligned with Thailand’s National AI Strategy and AIGC principles to ensure long-term governance, ethical use, and regulatory compliance. |
PTT Group has established the War Room 2025 to monitor macroeconomic changes stemming from U.S. reciprocal tax policies and other geopolitical tension especially Iran–Israel confrontation and Thailand – Cambodia border dispute, assess the potential impacts on the country and PTT Group, and formulate appropriate response plans. The War Room is structured in five key workstreams including; The War Room workstream structure consists of a sponsor, a flagship group leader, and a workstream PMO for each workstream. Regular monthly meetings are held to report progress, flag issues, identify opportunities and threats, and prepare mitigation plans to address those issues. The information is then submitted to the cross-functional PMO for consolidation. The War Room progress updates are reported to PTTGMC on a monthly basis. |
Sensitivity Analysis and Stress Testing
PTT provides insights into its sensitivity analysis and stress testing concerning financial risks, including foreign exchange rates, interest rates, and product prices, in the 56-1 One Report 2024: Financial Report, pages 202-203.
Furthermore, PTT has developed business plans to manage a range of potential scenarios (Scenario Planning), including various oil price levels. These plans ensure prompt and efficient responses to future uncertainties and changes. To enhance risk management, a dedicated Price Strategy and Risk Management Task Force has been established under the Petrochemical and Refining Integrated Synergy Management (PRISM) project. This team is responsible for analyzing global oil price fluctuations and managing price risks (Hedging) within the PTT Group. Currently, the PTT Group manages petroleum and petrochemical price risks using derivatives, with a comprehensive analysis and selection of appropriate tools tailored to specific timeframes and objectives (56-1 One Report 2024, pages 61, 63-64).
For further details on the risk factors impacting the Company’s operations in 2024, please refer to the 56-1 One Report 2024, pages 58-64.
Business Continuity Management
Business Continuity Management Process
PTT has developed a comprehensive Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) based on the ISO 22301:2019 standard and other relevant guidelines. The system encompasses prevention, response, recovery, and restoration, divided into three phases: the Prevention/Preparation phase, the Response/Continuity phase, and the Recovery phase. The Business Continuity Plan (BCP) has been approved by both the Management Committee and the PTT Board of Directors. In today's rapidly evolving environment, organizations face numerous challenges arising from unforeseen crises, including natural disasters, political instability, terrorism, pandemics, and cyber threats, all of which could disrupt vital operations. If PTT is unable to restore its operations to normalcy, it could result in severe damage to assets and lives, and have a wide-reaching impact on the nation, society, communities, and all stakeholders. Recognizing the critical importance of preparedness, PTT has prioritized the development of strategies to ensure a swift and effective response to such crises, enabling business continuity. Consequently, PTT has established a clear Business Continuity Management policy, requiring all management, employees, and partners to actively engage in and support the implementation of this policy consistently.
PTT has developed a comprehensive safety preparedness and emergency/crisis response plan, which is classified into four levels based on the severity of the event. In cases where external assistance is required from local, provincial, regional, or national agencies, the emergency/crisis situation will be escalated through levels 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. For each level, an Emergency/Crisis Management and Business Continuity Center is activated, with clearly designated responsible individuals and the appropriate delegation of authority at each level. This ensures that issues are resolved efficiently and that responses are prompt and coordinated with both public and private sector entities, as well as surrounding communities. Additionally, PTT has appointed departmental coordinators who act as liaisons to facilitate the Communication of critical information, such as required employee actions, key contact numbers, backup work locations, and significant annual updates. To further support emergency and business continuity management, PTT has developed an Emergency & Business Continuity Management Web Portal, which serves as a central communication hub for managing emergency/crisis situations and maintaining business continuity.
In 2024, PTT conducted a simulation exercise based on a scenario in which the LNG station Map Ta Phut Terminal 1 (LMPT1) of PTTLNG was set on fire and its natural gas pipeline was sabotaged. This situation required the management of the disruption to natural gas supply in the Eastern region, affecting multiple sources. The exercise was led by the CEO and President, with key executives from the Crisis Management Center (CMC) actively participating. The coordination was extended to the business group’s Emergency Management Center through a video conferencing system. Additionally, PTT continues to maintain its ISO 22301 Business Continuity Management certification, which covers the management of the Company’s utility systems. This certification is consistently upheld by the Thailand Industrial Standards Institute (TISI).