| Sustainable Development Goals |
Driving Strategies for Business Sustainability
Vision, Strategy, and Business Direction of the PTT Group GRI 2-22
In response to the fluctuating economic landscape, prolonged geopolitical tensions, energy price uncertainties, raw material volatility, and technological advancements, PTT Group is also navigating the global shift toward clean energy. This includes addressing the growing urgency of climate change and the worldwide commitment to achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, PTT faces challenges posed by evolving policies, regulations, and structural changes within the petrochemical and refining sectors. As a national energy company, PTT's mission is to ensure energy security for the country while maintaining a balanced approach to its diverse stakeholders.
In light of these factors and PTT’s mission as the national energy company, committed to ensuring the country’s energy security while balancing the interests of all stakeholders, the Company has carefully assessed the risks and opportunities ahead. This has led to a strategic recalibration, where PTT focuses on its core businesses—leveraging its expertise in areas directly impacting the nation—and embeds sustainability principles throughout its operations as follows:
- Vision: "Together for Sustainable Thailand, Sustainable World”
- Mission: To conduct integrated energy and related business as a National Energy Company, while delivering values to all stakeholders with balanced and sustainable approach. We focus on maintaining a balance and sustainability for all stakeholders, while adapting to the dynamic global landscape. We emphasize responsible business practices that consider social, environmental, and stakeholder interests, including government agencies, communities, investors, customers, partners, and collaborators.
- Strategic Direction: PTT is committed to ensuring energy security and sustainable growth, while achieving a balanced reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. The Company strives to achieve success by harmonizing the pursuit of profitability with the long-term goal of sustainability, aiming for Net Zero Emissions by 2050. This will be driven through five core strategies, as follows:
 |
- Competitive Enhancement: Existing Business
PTT is committed to strengthening the competitiveness of its existing businesses by prioritizing cost management and securing competitively sourced resources. This strategy is focused on two core business segments:
Hydrocarbon & Power Business
- Petroleum Exploration and Production (E&P) and Natural Gas
PTT is dedicated to ensuring energy security by focusing on continuity and stability in the supply of raw materials. This involves sourcing energy from new, competitive, and cost-effective sources. The Company is also actively advancing the Overlapping Claims Area (OCA) in the Thailand-Cambodia maritime region and expanding its investments in the LNG value chain. Each business unit is clearly defined to foster synergies within the PTT Group.
- Power Business
The focus is on maintaining stability in electricity generation and improving the efficiency of power plants, while sourcing clean energy to support the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions (Decarbonization) for the PTT Group. This is achieved through a transition in the energy mix for power production and exploring growth opportunities both domestically and internationally, with a strong emphasis on achieving optimal returns.
- Downstream Business
PTT prioritizes internal synergies within the Group to maximize value creation.
o Petrochemicals and Refining Business
PTT is optimizing its portfolio and forging strategic partnerships to stay adaptable to market shifts and improve its competitive edge.
o International Trading Business
The focus is on securing competitive feedstock for PTT's operations.
o Oil and Retail Business
PTT aims to become the trusted mobility partner for the Thai population, with a clear investment strategy focused on an Asset-Light approach.
Non-Hydrocarbon Business
In the past 3-4 years, PTT has invested in non-hydrocarbon businesses to align with emerging megatrends and government policies. However, given the current business environment, characterized by intense competition and rapid technological and market changes, PTT recognizes the need to reassess its non-hydrocarbon business strategy. This reassessment will be based on two main factors: business attractiveness and the potential for generating appropriate returns. PTT focuses on areas where it possesses strengths and the ability to capitalize on new opportunities (Right to Play). Additionally, PTT will evaluate the need for a well-structured management framework, ensuring collaboration with specialized partners to mitigate business risks and maximize value creation within the PTT Group.
- Growth: Necessity & Opportunity
PTT is committed to fostering growth in the hydrogen and carbon sectors through an integrated approach. This includes advancing hydrogen development and implementing Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technologies to capture and reduce CO2 emissions across the PTT Group. Furthermore, the roles within the PTT Group are clearly defined, with PTT serving as the key integrator, leveraging the unique strengths of each subsidiary for optimal impact. The PTT Group aims to be a national leader in the transition to achieving Net Zero Emissions.
- Sustainability: Unleash Business Values through Sustainability
PTT is committed to balancing business growth with sustainable outcomes by focusing on the key ESG pillars: Environmental (E), Social (S), and Governance (G). The Company aligns its portfolio management and Net Zero Emissions targets across all divisions, while driving sustainability efforts through a comprehensive Sustainability Framework.
- Enablers for Transformation
PTT is committed to advancing operational excellence by strengthening internal capabilities, enhancing operational efficiency, and boosting competitiveness across all areas, such as marketing and sales, production processes, maintenance, and procurement. Additionally, PTT sets a unified EBITDA uplift target for the entire PTT Group. The Company also places a strong focus on:
✅ Developing employee potential
✅ Restructuring the organization into a Lean Organization
✅ Transforming processes through digital technology (Digital Transformation)
✅ Utilizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) to drive operational improvements
PTT aims to build a robust organizational culture, encouraging employees to be aware of and embrace change, fostering sustainable growth under the framework of People, Organization, and Digital Transformation.
- Foundation
PTT is committed to upholding strong governance and best practices in corporate management, alongside financial excellence. This includes strategically monetizing non-revenue-generating assets to enhance profitability and stabilize cash flow, ensuring PTT’s ability to operate sustainably and securely over the long term.
Responsibility to Vision and Strategic Drive for Business Sustainability
Aligned with this vision and strategic direction, PTT has established the PTT Sustainability Management Framework, which integrates investment management, carbon management, and sustainability management in a balanced and harmonious way. This framework also focuses on managing greenhouse gas emissions to meet reduction targets, utilizing the appropriate tools and methodologies to maintain competitive advantage while fostering continuous growth. For other critical sustainability issues, PTT continues to drive systematic processes and improvements, ensuring the creation of long-term value effectively and efficiently. The Company’s goal is to achieve top-tier ESG ratings, ranking in the top 5% within its industry.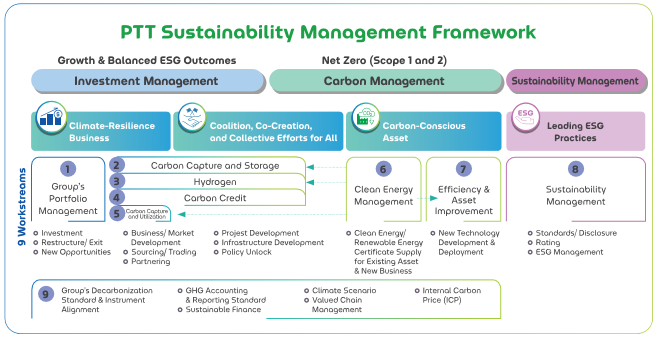 |
To bring the vision, strategic direction, and goals into practice across the organization, they have been translated into the 2025-2029 Business Plan, operational plans, key performance indicators (KPIs), and target values. These elements are integrated into various processes, such as investment decision-making, business model development, product and service design, departmental workflows, and the management of key sustainability issues, ensuring alignment at every level.
Under the vision “Together for a Sustainable Thailand, Sustainable World,” PTT is committed not only to ensuring the country’s energy security but also to growing sustainably on a global scale. This growth takes into account the environmental and social impacts, while simultaneously focusing on generating profits. To achieve this, PTT has developed the “Sustainability Management Master Plan, reflecting PTT’s responsibility to society and the environment from 2021 to 2025.” The plan defines the “Sustainability Strategy Direction,” which encompasses three main dimensions: Environmental, Social, and Governance & Economic. Clear indicators, short-term, medium-term, and long-term goals, as well as strategies for success, have been established. The goal is to gain international recognition in sustainability and to achieve the highest level of ESG performance. The strategy aligns with the national 20-year development plan and supports the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), as outlined below:
-01.png) |
Supporting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
PTT regularly reviews the priority SDGs that are most relevant to its business operations, using them as a guide for planning and executing activities. The review process consists of three key steps:
- Assess key internal and external factors, including the organization’s vision, strategic direction, critical sustainability issues, sustainability-related policies, strategies, goals, and action plans. This also involves examining global sustainability trends and changes that could impact business operations throughout the entire value chain, as well as understanding the needs and expectations of stakeholders.
- Prioritize and evaluate responses to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), referencing international SDG implementation guides, such as the SDG Ambition Integration Guide, the SDG Compass by the UN Global Compact, IPIECA’s Mapping the Oil and Gas Industry to the SDGs: An Atlas, WBCSD’s SDG Sector Roadmaps, and the Accelerating Action: An SDG Roadmap for the Oil and Gas Sector by IPIECA and WBCSD. This process should also align with national strategic frameworks, such as the 20-Year National Strategy (2018-2037) and the 13th National Economic and Social Development Plan (2023-2027), which are relevant to PTT’s operations. The SDGs are then categorized into two groups: 11 goals to be integrated into the organization’s core business operations (Integrate into Core Business) and 6 goals to be pursued through collaboration with sustainability networks or engagement with relevant stakeholders (Collaborate with Other Stakeholders).
- Communicate and clarify the prioritization and implementation approach to relevant departments, providing them with a clear framework for developing business plans, initiatives, and projects that support the management of key sustainability issues. Additionally, this should include strategies for fostering relationships with stakeholders in the relevant areas.
Governance Structure and Responsible Business Practices
Sustainability Governance StructureGRI 2-9, GRI 2-13
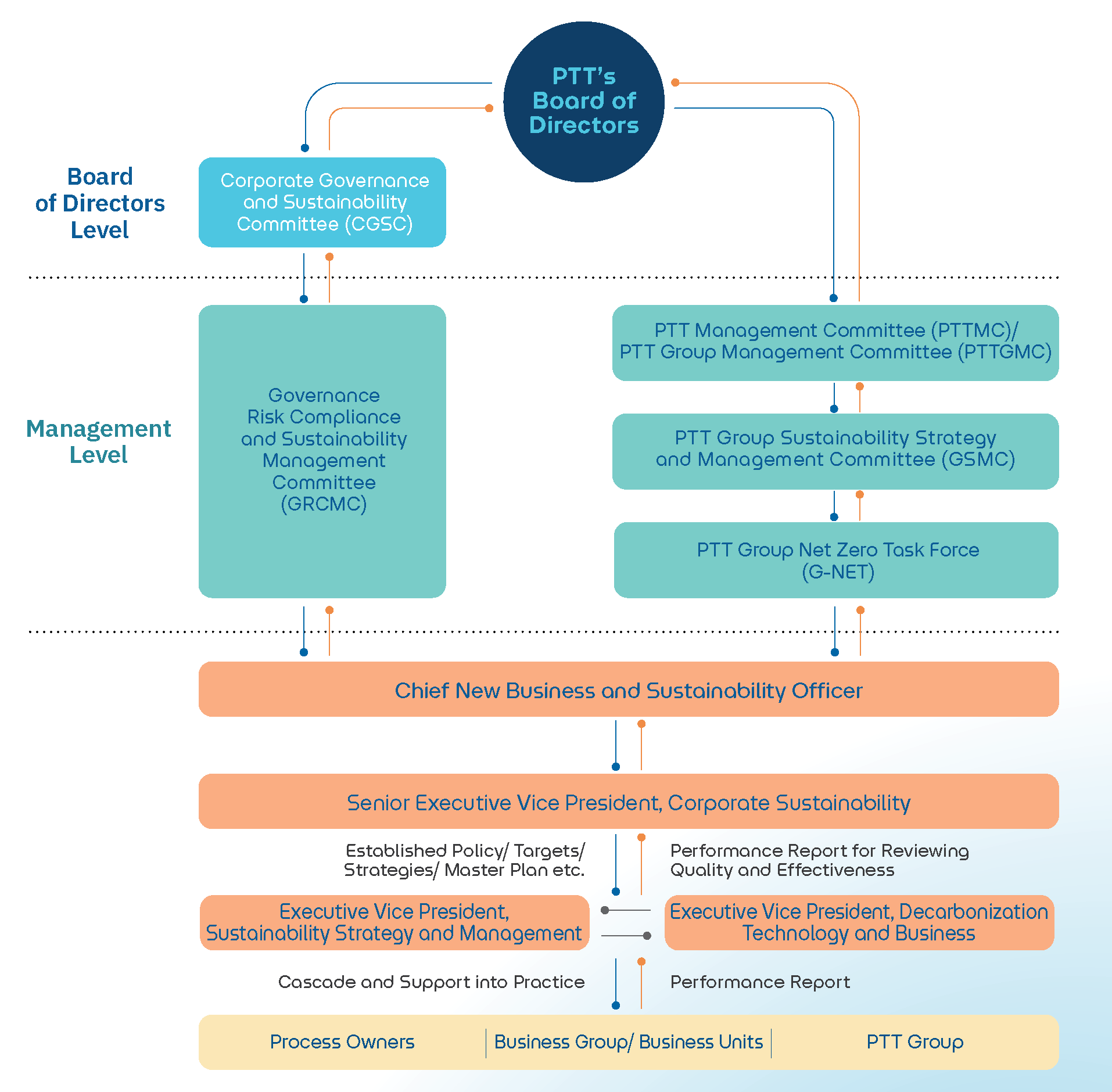 |
PTT has established a comprehensive governance structure to drive the business toward sustainability, with clearly defined roles and responsibilities at all levels, including the Board of Directors, management, executives, and internal departments. This structure ensures the effective and efficient management of sustainability by facilitating the support, monitoring, and review of the overall sustainability efforts to achieve the set goals. The performance results are compiled, analyzed, and reported quarterly to various working groups and committees, such as the G-NET (Greenhouse Gas Net Zero Committee) of PTT Group, the GRCMC (Governance, Risk, Compliance, and Sustainability Management Committee), the GSMC (PTT Group Sustainability Strategy and Management Committee), and the CGSC (Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee). In addition, an annual performance report, sustainability management process review, and sustainability management plan are presented to the PTT Board of Directors.
To effectively implement the newly defined vision, strategic direction, and sustainability framework, PTT has established the position of Executive Vice President for Corporate Sustainability, reporting to the Chief Operating Officer of New Business and Sustainability. This position oversees two key divisions: Assistant Executive Vice President for Strategy and Sustainability Management, responsible for defining and driving the policies, strategies, master plans, and various initiatives across the entire organization and PTT Group; and Assistant Executive Vice President for Technology and Carbon Reduction Business, focused on researching and developing Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) and hydrogen businesses, in collaboration with the PTT Group.
Each key sustainability issue is assigned to a specific department for management, with oversight provided by both management and the PTT Board of Directors. Further details can be found in the section on Processes and Evaluation Results for Key Sustainability Issues.
Responsible Business Operations PolicyGRI 2-9, GRI 2-13
PTT is deeply committed to conducting business responsibly and has expressed this commitment through several key policies, as outlined below:
- PTT’s Sustainability Management Policy, signed by the Chairperson of the Board of Directors and the Chief Executive Officer of PTT Public Company Limited. This policy outlines the organization’s intent to manage sustainability across three key dimensions: environmental, social, and governance.
- PTT’s Corporate Governance Policy, signed by the Chairperson of the Board of Directors of PTT Public Company Limited, aims to establish PTT as an efficient organization that excels in business operations, corporate governance, and management. The focus is on creating long-term value for shareholders while considering the interests of all stakeholders, promoting ethical business practices, and ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Human Rights Statement, signed by the Chief Executive Officer and the President of PTT Public Company Limited.
Additionally, PTT has developed specific policies to further demonstrate its commitment to managing critical issues in a clear and appropriate manner. These include:
- Quality, Security, Health, Safety, and Environmental Policy for the PTT Group
- Stakeholder Management Policy for PTT
- Anti-Corruption and Anti-Bribery Policy for PTT Public Company Limited
All policies are reviewed annually to ensure they remain aligned with changing circumstances and evolving sustainability issues within the organization.
Corporate Governance of PTT GroupGRI 2-24
PTT has established a comprehensive corporate governance framework for the PTT Group, referred to as the PTT Group Way of Conduct. This framework consolidates guidelines, best practices, and operational processes across all areas of PTT and its subsidiaries to ensure alignment and coordination within the group. It serves as a governing tool for companies in which PTT holds shares, ensuring the implementation of consistent standards across the entire group. These practices are carried out by PTT representatives, who are assigned roles as directors, executives, and staff, thereby ensuring that the PTT Group operates cohesively. This approach fosters collective strength, enhances global competitiveness, and supports transparent and sustainable growth for the PTT Group.
PTT Sustainability Management Standard
In 2021, PTT reviewed and updated the PTT Group Sustainability Management Framework from 2016 into the “PTT Sustainability Management Standard.” This revision was made to align with both national and international standards, ensuring that the framework remains current and adaptable. It incorporates global best practices, including ISO 26000 (on social responsibility), the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC), the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) standards, and the State Enterprise Assessment Method (SE-AM), among others. The updated standard is structured into three key components:
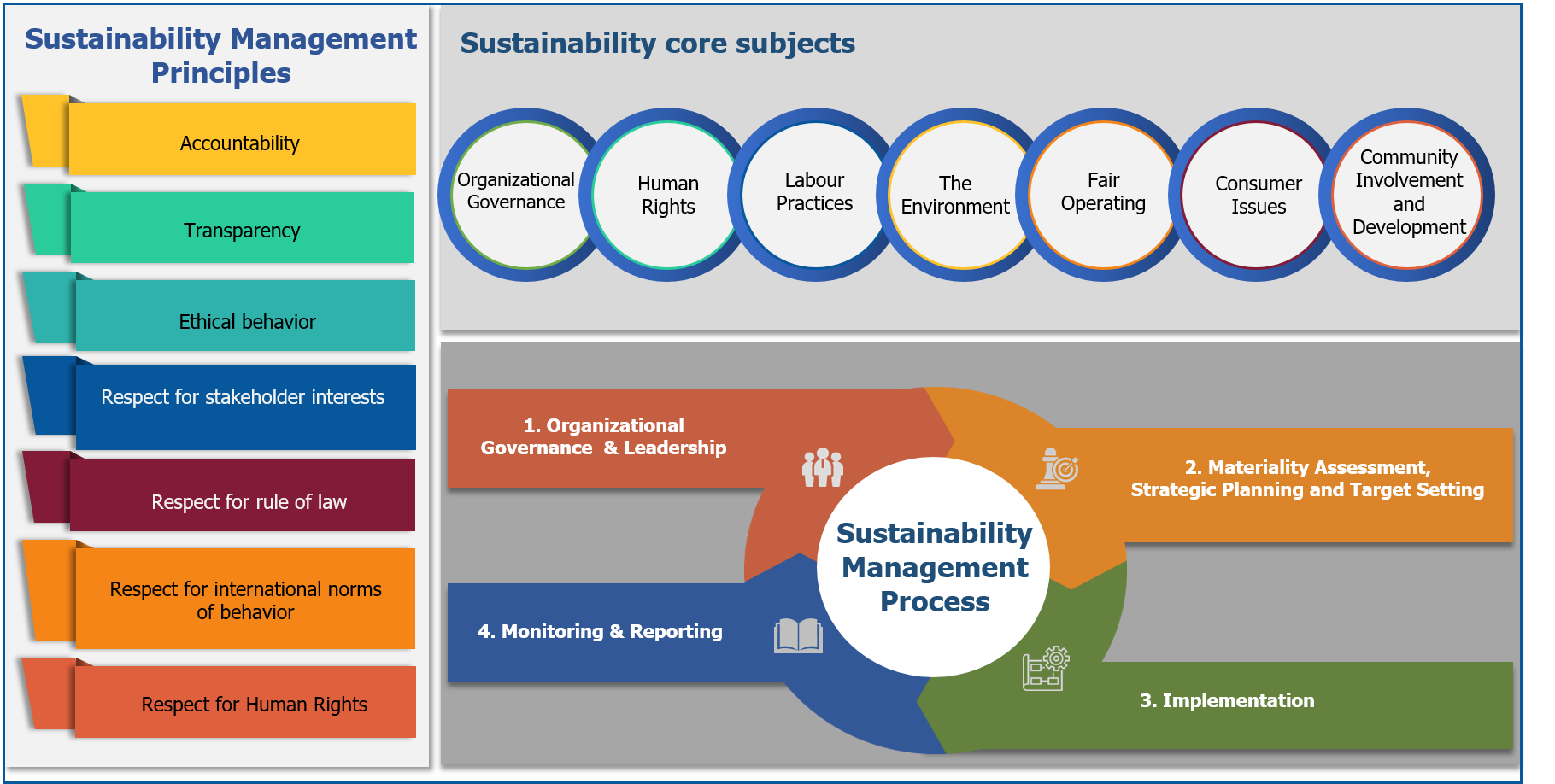 |
1. Principles of Sustainability Management, consisting of 7 key principles:
- Accountability: Ensuring proper governance alongside the management of risks and opportunities, addressing critical sustainability issues, and establishing an effective governance structure.
- Transparency: Providing clear, accurate, timely, and comprehensive disclosure of organizational activities that impact the economy, society, and the environment.
- Ethical behavior: Upholding fair business practices in all agreements to prevent creating imbalances that could disadvantage other organizations or consumers.
- Respect for Stakeholder Interests: Actively engaging stakeholders in a fair and efficient manner, ensuring full and transparent feedback.
- Respect for the Rule of Law: Complying with applicable laws, regulations, and requirements, with regular reviews to ensure adherence to legal standards.
- Respect for International Norms of behavior: Following legal standards and avoiding involvement in activities that do not align with international guidelines and practices.
- Respect for Human Rights: Safeguarding the human rights of all individuals affected, both positively and negatively, by the organization’s business operations.
2. Key Sustainability Topics, consisting of 7 core areas:
1) Organizational Governance
2) Human Rights
3) Labor Practices
4) The Environment
5) Fair Operating
6) Consumer Issues
7) Community Improvement and Development
3. Sustainability Management Process, consisting of 4 stages:
| Procedures | Description |
|---|---|
1. Organizational Governance & Leadership |
|
2. Materiality Assessment, Strategic Planning and Target Setting |
|
3. Implementation |
|
4. Monitoring and Reporting |
|
Evaluation of Key Sustainability IssuesGRI 3-1, GRI 3-2
PTT's process for evaluating key sustainability issues is aligned with the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Universal Standards 2021 and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). It is designed to identify both risks and opportunities related to sustainability, covering the environmental, social, and governance dimensions. The evaluation emphasizes human rights throughout the organization’s operations, assessing both actual and potential positive and negative impacts. These impacts are considered in relation to stakeholders, society, and the environment (Impact Materiality), as well as the external factors that affect financial performance and value creation (Financial Materiality) across the entire value chain. The evaluation follows the principles of Double and Dynamic Materiality, ensuring a comprehensive approach that integrates with the organization’s annual risk assessment process. This approach allows for the ongoing review of changes in impacts, considering evolving internal and external factors, and adapting to changing circumstances. The process consists of the following 4 main steps:
 |
Step 1: Understand the Organization's Context
Consider both internal factors (e.g., vision, strategic objectives, organizational risks, operations/activities, etc.) and external factors (e.g., standards, regulations, best practices, global trends, and related risks). Additionally, evaluate the sustainability issues of PTT, its subsidiaries, and companies within the relevant industry. This includes analyzing stakeholder needs and expectations across the value chain, based on feedback collected through surveys, consultations, and interviews with key stakeholders. The goal is to gather, categorize, and identify key sustainability issues.
Step 2: Identify Actual and Potential Impacts
Identify both the positive and negative impacts, both present and potential future, arising from sustainability issues, covering environmental, social, and governance aspects. This process should take into account human rights impacts throughout the organization's operations. Begin by identifying negative impacts—current and future—that the organization directly causes, participates in, or is linked to through its business activities along its value chain. Then, identify the positive impacts—current and future—that contribute value to sustainable development.
Step 3: Assess the Significance Impacts for Reporting
Evaluate the materiality of impacts on society and the environment (Impact Materiality) as well as their effects on the organization’s financial performance (Financial Materiality) through both quantitative and qualitative analysis of both negative and positive impacts. Additionally, consider the significance of issues or impacts that may evolve over time. Issues that currently have no immediate effect could have significant implications for the business in the future.
Negative Impacts: Assess the materiality of actual negative impacts by evaluating their severity, which includes their scope, intensity, and recoverability. Also, consider potential future negative impacts, assessing their likelihood and severity.
Positive Impacts: Assess the materiality of positive impacts by evaluating their scale and scope. Similarly, assess potential future positive impacts based on their scale, scope, and likelihood of occurrence.
Step 4: Prioritize the Most Significant Impacts for Reporting
The impacts are prioritized, and key sustainability issues are selected based on an analysis of their effects on society and the environment (Impact Materiality) and their potential influence on the organization’s financial performance (Financial Materiality). These issues will be managed and disclosed in the 56-1 One Report and on PTT's website in an appropriate manner. The evaluation results have been reviewed collaboratively with relevant departments and experts. All processes are governed and approved by PTT's management board and Board of Directors, including the Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance Committee, and the Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee, respectively. Furthermore, external experts and agencies are engaged to audit the process and validate the material sustainability issues to ensure completeness, accuracy, reliability, and transparency. PTT takes into account feedback from these experts and external agencies to continuously refine and improve its operational processes and data disclosure practices.
2024 Sustainability Materiality Assessment ResultsGRI 3-2, GRI 3-3
The 2024 sustainability materiality assessment highlights key issues from both Impact Materiality (social and environmental impacts) and Financial Materiality (impacts on organizational financial performance). The top three priorities identified are as follows:
Climate Action remains the top priority for the organization due to its far-reaching impact on the environment, society, and the economy. The energy sector, as a major emitter of greenhouse gases, faces increasing pressure from stakeholders and the implementation of stricter regulations (e.g., Net Zero Guidelines, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), GRI, and Draft Thailand’s Climate Change Act) which will be effective in the future. From the financial materiality perspective, climate change risks impact the organization’s cost structure, disrupt business operations, and pose increased financial risks. Moreover, stakeholders such as investors and customers expect the organization to play a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Delayed actions in addressing climate change could damage the company’s reputation. However, investments in clean energy and energy efficiency improvements present an opportunity to reduce operational costs, generate new revenue streams, and strengthen competitiveness. From the impact materiality perspective, the negative impacts include ecosystem degradation, biodiversity loss, and challenges to the quality of life in surrounding communities, such as food and water insecurity.
| Key Sustainability Issues | Impact on Business* | Business Strategy | Additional Management Information |
| Climate Change Management |
〇 Cost |
|
Click |
| *The positive and negative impacts are shown in the table of impacts and sustainability issue management. | |||
Innovation and Technology are vital drivers in transforming and expanding the business to support the energy transition and respond to the changing demands of consumers. Promoting creativity and innovation within the organization is key to improving operational efficiency, enhancing competitiveness, and opening up new revenue opportunities. In terms of financial materiality, innovation and technology can reduce operational costs, boost performance, and generate income from new business ventures. Furthermore, innovation supports business resilience by allowing the company to better navigate market fluctuations and environmental regulatory challenges. Failure to adapt to technological trends could lead to financial risks and a loss of competitive advantage. For impact materiality, innovation plays an essential role in developing products and services that reduce carbon emissions, support a low-carbon transition, and address stakeholder expectations, such as customers, investors, and communities. Operations focused on innovation, therefore, have the potential to create positive impacts on society and the environment in the long term.
| Key Sustainability Issues | Impact on Business* | Business Strategy | Additional Management Information |
| Innovation and Technology | 〇 Cost ✔ Revenue 〇 Risk |
|
Click |
| *The positive and negative impacts are shown in the table of impacts and sustainability issue management. | |||
Occupational Health and Safety workplace safety is a critical factor in preventing accidents and injuries that may occur to employees, contractors, and surrounding communities. Not only does it affect the quality of life of personnel, but it also has a direct impact on the efficiency and continuity of business operations within the organization. Therefore, in terms of financial materiality, strict occupational health and safety management helps reduce costs from accidents and illnesses, such as insurance premiums, medical expenses, and compensation, as well as minimize disruptions to production processes, which reflect income loss and increased costs. For impact materiality, stakeholders such as employees, contractors, and nearby communities may face irreversible health and safety risks, leading to uncertainty in the operational system and creating concerns within the community.
| Key Sustainability Issues | Impact on Business* | Business Strategy | Additional Management Information |
| Occupational Health and Safety |
✔ Cost |
|
Click |
| *The positive and negative impacts are shown in the table of impacts and sustainability issue management. | |||
Impact and Management of Key Sustainability Issues
Material Topic Impacts and Management
Targets and Key Indicators for Material Topics
| Material Topics | Targets | Performance against 2024 Targets | Indicators | |
| Short-term (By 2024) | Long-term | |||
| Climate Action |
|
|
|
|
| Innovation and Technology |
|
|
|
|
| Occupational Health and Safety |
|
Target for 2030: All indicators are to be zero. |
|
|
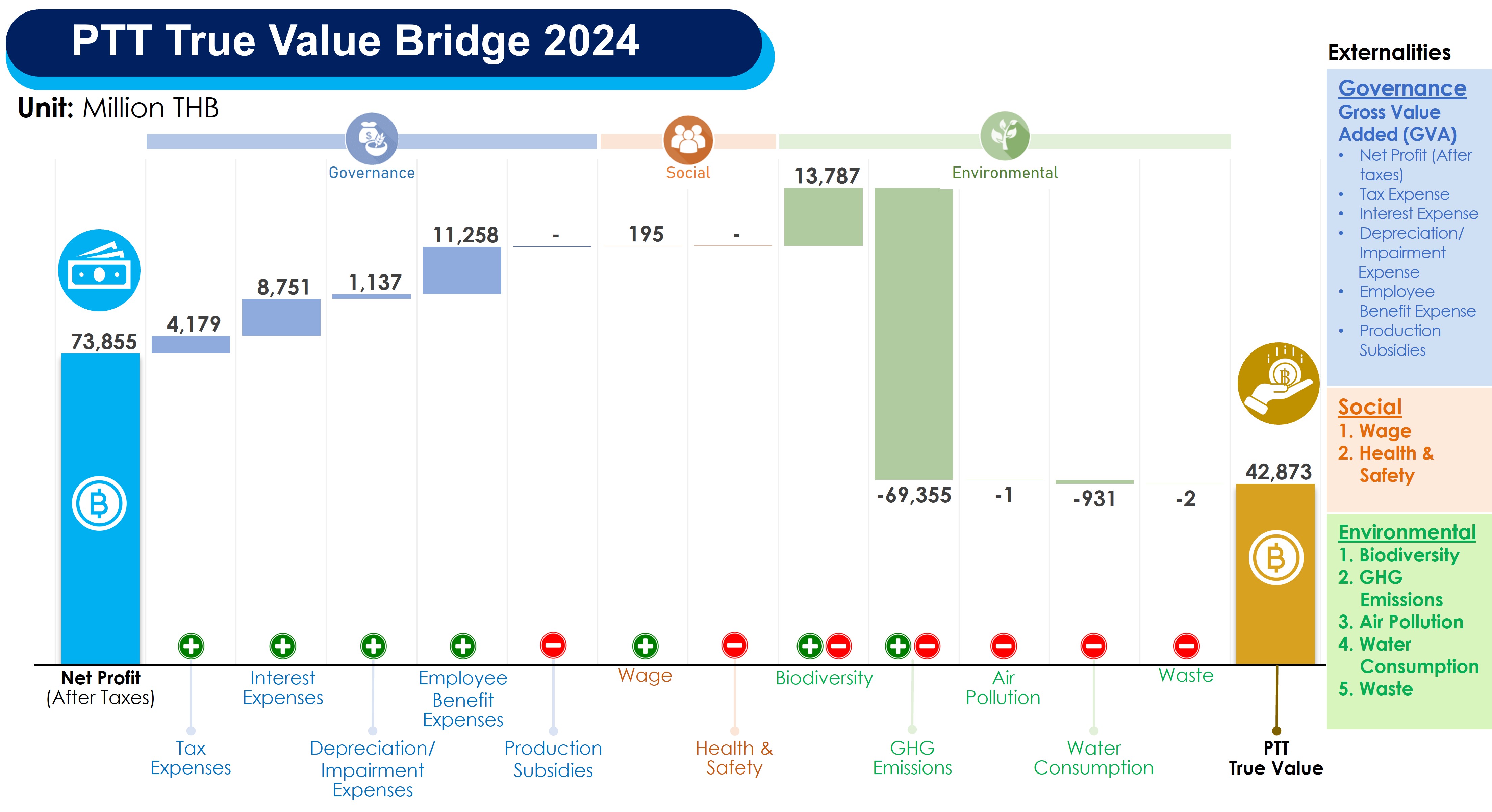
True Value Assessment of the Organization from Sustainability Management Results
PTT evaluates the true value of the organization based on both positive and negative sustainability impacts, encompassing the environmental, social, and governance dimensions. This evaluation helps stakeholders gain a clear and accurate understanding of the organization’s performance, highlighting both the positive and negative externalities from its operations in financial terms. Additionally, it provides the company with opportunities to improve its operations, reduce negative impacts, and mitigate risks that may affect the business and its stakeholders. This process leads to better management practices and serves as a foundation for planning and decision-making for future company initiatives.
The real sustainability value assessment of the organization is conducted in five main steps. The scope of the assessment includes the operational performance data of PTT for each year (excluding companies within the PTT Group) as follows:
- Review the policies, strategies, and action plans related to sustainability management within the organization.
- Identify the most significant sustainability issues for the organization each year and define indicators that reflect both direct and indirect impacts.
- Collect data on these indicators and the corresponding value variables to analyze both positive and negative impacts, including direct and indirect effects.
- Calculate the value of sustainability impacts, both positive and negative, by multiplying the quantitative sustainability performance data by the value variables of the indicators.
- Aggregate the values of each indicator—both positive and negative impacts—to determine the organization’s true value.
 |
| Externalities and Impact on External Stakeholders | Output Metric | Impact Valuation | Impact Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Governance Dimension |
|||
|
Gross Value Added (GVA) GVA is a measurement of the contribution to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) made by an individual producer, industry, or sector. |
Baht |
Direct way, such as net profit (after taxes), providing wages and other benefits to employees, and paying taxes to local governments. |
Baht |
|
Social Dimension |
|||
|
Wage Wage can be defined as “a basic but decent level of life that allows a household to get good nutrition, housing, health and education”. Societal impacts arising from paid salaries to employees in PTT’s own operations were compared to the living wage on country level. |
Baht |
DALY (Disability Adjusted Life Years) for negative impacts and QALY (Quality Adjusted Life Years) for positive impacts |
Baht |
|
Health & Safety The scope of occupational health and safety covers work related injuries, illnesses and deaths of employees and contractors which impose costs on workers and the community. The social cost is measured from indirect costs that include items such as lost productivity, loss of current and future earnings, lost potential output, and the cost of providing social welfare programs for injured or incapacitated workers. |
Number and type of occupational incidents | Worker and community cost/ incident | Baht/ incident |
|
Environmental Dimension |
|||
|
Biodiversity The transformation of land by a company can positively and/ or negatively affect the functioning ecosystems and the life of local communities depending on the land use management. The impact of PTT’s land use on biodiversity is assessed by using estimated annual benefits from the ecosystem services in different ecosystems. The rehabilitated area is a representation for the positive cost and the disturbed area is negative cost. |
Hectare | Environmental cost of ecosystem degradation/ restoration | Baht/ hectare |
|
GHG emissions The release of greenhouse gases primarily drives climate change, leading to severe impacts on both society and the environment. Negatively, it triggers extreme weather events and rising sea levels that threaten human health, disrupt economies, and damage ecosystems. These changes strain infrastructure and agriculture, increasing food insecurity and migration. Positively, the global response to climate change has spurred innovations in energy efficiency and renewable technologies. This transition not only mitigates further environmental damage but also promotes economic opportunities and enhances ecosystem resilience through restoration and adaptation measures. |
Ton CO2e |
Social cost of carbon | Baht/ ton CO2e |
|
Air pollution Cost from air pollutants including impacts on health, crops & forests, ecosystems, and material damage. |
Ton of NOx, SO2 and VOCs | Social cost of emissions | Baht/ ton emissions |
|
Water consumption The social cost of water adjusted for purchasing power parity which depends on the water scarcity level area. |
m3 | Purchasing power parity | Baht/m3 |
|
Waste Waste treatment can affect the society and environment (i.e. incineration lead to GHG emission, landfill lead to methane and contaminate groundwater etc.) |
ตัน | Societal cost of waste/type and treatment type | Baht/ ton |

